External Translation using XLIFF
Translations for Scroll Documents allows for external content translation though the use of the XLIFF file format.
Why Use External Translation?
When localizing product documentation, oftentimes not all target languages can be handled internally, requiring cooperation with professional translation providers. The export of content for translation and the re-import of content after its translation can be difficult to manage in the authoring system. In order to solve this problem, Translations for Scroll Documents enables the export and import of Scroll Documents as XLIFF files.
The XML Localization Interchange File Format (XLIFF) is an XML-based file format that is frequently used by computer-aided translation tools. (Official documentation)
During the XLIFF export, each page is broken up into smaller text pieces, so-called translation units, which can be translated separately by your translation provider. Besides actual text paragraphs, table contents and certain macro parameters are also extracted to be translated. The translations are done within the XLIFF files, meaning that once all XLIFFs are translated, you will receive a collection (ideally a ZIP) containing translated XLIFF files from your translation provider. Once this ZIP archive is uploaded, translated pages are re-assembled from the individual translation units, with the result resembling the source page, but with its text translated.
Recommended Authoring, Translation, and Publishing Flow
When implementing an initial setup for the authoring, localization and publishing of a documentation, we propose the following flow:
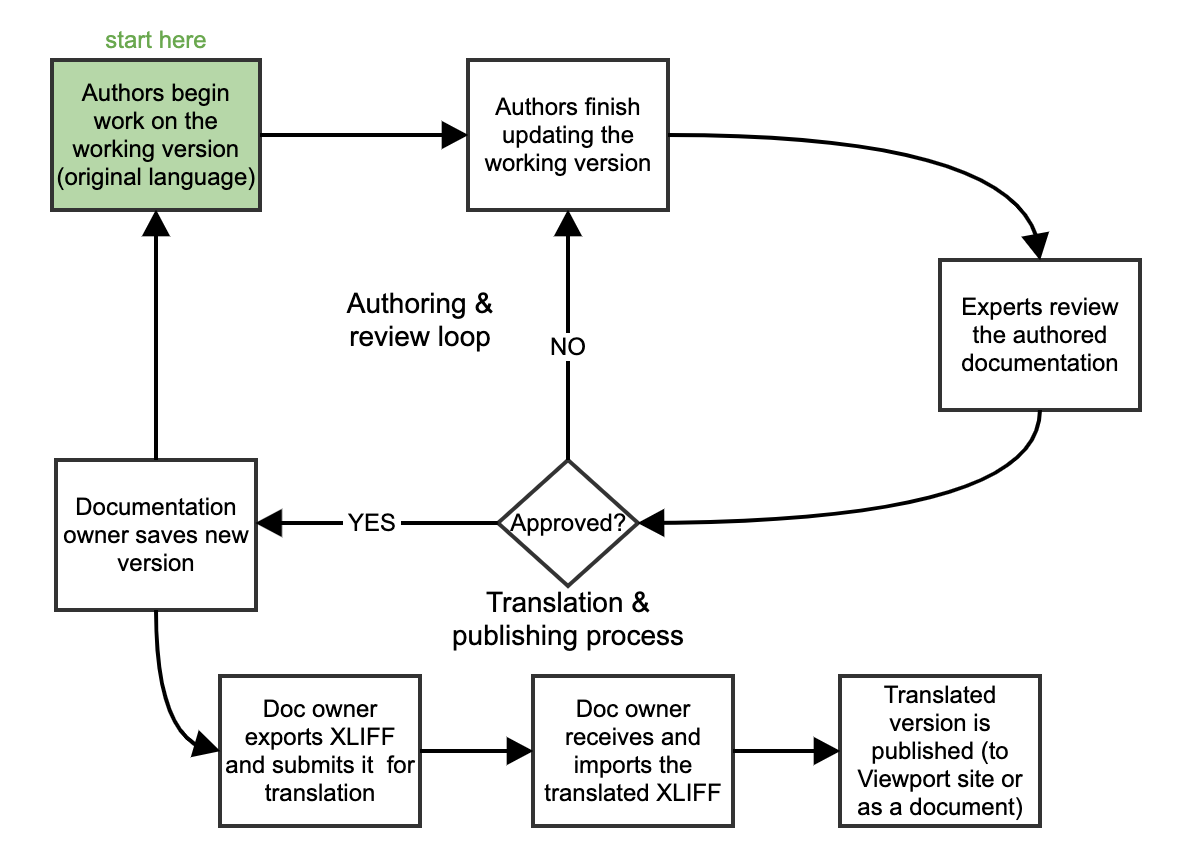
There are some notable points in the above flow:
Working version remains untranslated: Though technically possible, we recommend to not translate the working version and to keep it in the original authoring language only. This convention helps keep the authoring loop short and separate from the translation and publishing process, which means you're free to begin work on a new version of your documentation while external translation is still going on.
Translation memory is external: Translation providers generally make use of translation memory, which "remembers" previously translated content and prevents re-translation of content. Translations for Scroll Documents does not provide any translation memory, meaning it needs to be translated by the translation provider.
